Until recently, the traditional hospital data center featured a conventional three-tiered infrastructure, where compute, storage, and network resources were all managed separately. This environment required multiple IT staff with specialized skills—a luxury many hospitals do not have. But times are changing.
Personalized medicine is already here
Today’s approach to healthcare is very different from centuries ago, or even a few decades ago. For example, cancer once was thought to be something that just happened, and beyond radical surgery – which came with its own risks – there wasn’t much you could do about it. Thanks to much research, including genetic sequencing, and the application of technology like artificial intelligence to big data, we now know that there are genetic, environmental, and physiological contributors to various types of cancer. Recently, doctors have started to use DNA analysis to develop personalized diets and medication regimens to help patients deal more easily with chemotherapy and radiation. This targeted approach, which varies from patient to patient, can lead to more positive patient outcomes. Treatment of other diseases and conditions, such as migraines, attention deficit disorder, and neurodegenerative diseases like multiple sclerosis can also benefit from personalized medicine.
But what about personalized IT?
While the field of healthcare continues to evolve toward a personalized view, the infrastructure that supports healthcare—healthcare IT—has primarily retained a one-size-fits-all perspective that hinders agility, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Until recently, the traditional hospital data center featured a conventional three-tiered infrastructure, where compute, storage, and network resources were all managed separately. This environment requires multiple IT staff with specialized skills—a luxury many hospitals do not have.
To address the inefficiencies associated with a three-tiered infrastructure, many hospitals have turned to hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI). In an HCI environment, compute, storage, and network resources are all brought into a single management plane. This simplifies the IT workload but is not a universal remedy. First-generation HCI assumes that IT resources all need to scale at the same pace. If you add storage, you also add compute and network resources. In reality, especially with electronic health records growing larger and more complex, data storage demand can far outpace compute demand. HCI can lead to inefficiencies by forcing hospitals to add compute and storage, when in some scenarios all they need is more storage.
Enter the disaggregated hyperconverged infrastructure (dHCI) solution from HPE and AMD
What if your healthcare organization could get all the management benefits of HCI but could still scale compute and storage separately? Now you can – with HPE Alletra dHCI. Essentially second-generation HCI, dHCI helps hospitals ease constrained resources by keeping the single-pane-of-glass approach for resource management but allowing independent scaling of compute and storage, which can help lower operational costs and reduce data center footprint. With dHCI, you can personalize your IT environment to fit your specific compute and storage needs.
Here are some of the highlights of this new generation of HCI:
- Simplicity. With an HPE dHCI solution, healthcare IT can deploy full-stack infrastructure in minutes using automation, with unified, self-service management. HPE InfoSight makes resource planning simple.
- Resiliency. HPE dHCI solutions are designed for 99.9999% availability to keep critical-to-care and office apps always-on and always-fast.
- Advanced security features. Patient data is well protected by innovative security features like HPE Silicon Root of Trust and AMD Infinity Guard, built right into the hardware.
- Efficiency. Scalable – without waste
- Cloud-like experience in your private data center. The HPE GreenLake edge-to-cloud platform provides the ability to pay only for what you use while keeping your data on-premises.
A closer look at dHCI
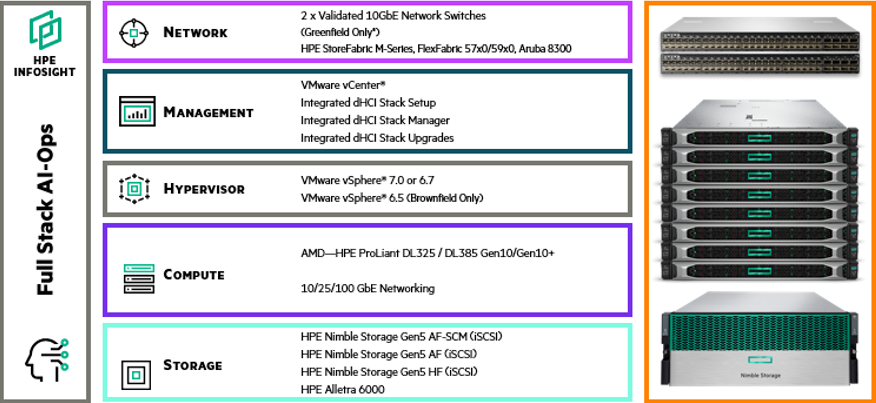
What exactly goes into an HPE Alletra dHCI deployment?
The solution includes several building blocks, including network, management, hypervisor, compute, and storage, all under the HPE InfoSight umbrella. The management and hypervisor are based on VMware products, like VMware vCenter and vSphere. The world record performance of the AMD EPYC™ processors provides the compute power healthcare providers need for high performance and the embedded security features required to keep patient data secure.
AMD EPYC processors have set more than 250 world records for compute performance.* These processors also provide a modern, multi-faceted approach to data center security with practically no impact on performance. AMD Infinity Guard helps shield system memory from attacks without having to add costs or code, while AMD Secure Encrypted Virtualization (SEV)** is designed to isolate VMs from the hypervisor, thereby increasing privacy and integrity. It encrypts each VM with a unique encryption key known only to the processor.
Hospitals can choose to deploy a greenfield HPD dHCI solution, starting from scratch, or they can choose to expand an existing dHCI .
Compute: HPE ProLiant DL325/DL385 Gen10 and Gen10 Plus servers_AMD EPYC™ Processors_10/25/100 GbE networking
HPE Alletra dHCI by the numbers
All the above discussion is well and good—but what does it all mean in terms of dollars and cents, uptime, and performance? According to a 2022 report from ESG Economics.*** HPE dHCI delivers up to lower total cost of ownership (TCO) while providing lower latency – better performance – and higher levels of resiliency. Specifically, admin costs were up to 53% lower and support costs up to 87% lower compared to traditional HCI deployments.
Consider what current users have to say:
In addition, HPE dHCI provides 10x faster application performance, 4x more reliability – designed for 99.9999% data availability – and 5x more efficiency, compared to traditional HCI.
Summary
HPE and AMD can help ease constrained resources in healthcare with dHCI — a simple, reliable, and secure infrastructure to run critical-to-care and workplace apps. It is a solution that makes storage and compute independently scalable to help lower TCO and reduce data center footprint so staff can focus on providing better care for their patients.
HPE and AMD understand the problems facing healthcare organizations today and are delivering groundbreaking IT solutions that can revolutionize the hospital data center.
To learn more:
- Visit www.hpe.com/info/healthcare and www.hpe.com/partners/amd.
- MD Infinity Guard features vary by EPYC processor generations. Infinity Guard features must be enabled by server OEMs and/or cloud service providers to operate. Check with your OEM or provider to confirm support of these features. https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/infinity-guard GD-183
- AMD EPYC processors have set more than 250 world records for compute performance. https://www.amd.com/en/processors/epyc-world-records
*Compares Dell EMC VxRail with HPE Alletra dHCI using 100 TB effective capacity, ability to withstand a minimum of two drive failures, and triple mirroring.
**Available with 2nd and 3rd Gen AMD EPYC processors.
***https://www.hpe.com/psnow/doc/a50005424enw